KNEE ARTHROSCOPIC
SURGERY
Knee arthroscopic surgery is a procedure
performed through small incisions in the skin to repair injuries to tissues such
as ligaments, cartilage, or bone within the knee joint area. The surgery is
conducted with the aid of an arthroscope, which is a very small instrument
guided by a lighted scope attached to a television monitor. Other instruments
are inserted through three incisions around the knee. Arthroscopic surgeries
range from minor procedures such as flushing or smoothing out bone surfaces or
tissue fragments (lavage and debridement ) associated with
osteoarthritis, to the realignment of a dislocated knee and ligament grafting
surgeries. The range of surgeries represents very different procedures, risks,
and aftercare requirements.
Purpose
There are many
procedures that currently fall under the general surgical category of knee
arthroscopy. They fall into roughly two groups—acute injuries that destabilize
the knee, and pain management for floating or displaced
cartilage and rough bone. Acute injuries are usually the result of traumatic
injury to the knee tissues such as ligaments and cartilage through accidents,
sports movements, and some overuse causes. Acute injuries involve damage to the
mechanical features, including ligaments and patella of the knee. These injuries
can result in knee instability, severe knee dislocations, and complete lack of
knee mobility. Ligament, tendon, and patella placements are key elements of the
surgery. The type of treatment for acute injuries
depends in large part on a strict grading system that rates the injury. For
instance, grades I and II call for rest, support by crutches or leg brace, pain
management, and rehabilitation. Grades III and IV indicate the need for surgery.
Acute injuries to the four stabilizing ligaments of the knee joint—the anterior cruciate ligament
(ACL), the posterior cruciate ligament
(PCL), the medial collateral ligament
(MCL), and the lateral collateral ligament
(LCL)—as well as to the "tracking," or seating of the patella, can be highly
debilitating.
Treatment of these
acute injuries include such common surgeries as:
- Repairs of a torn ligament or reconstruction of the ligament.
- Release of a malaligned kneecap. This involves tendon surgery to release and fit the patella better into its groove.
- Grafts to ligaments to support smoother tracking of the knee with the femur.
Treatment distinctions between arthroscopic surgery for
acute injuries and those for pain management are important and should be kept in
mind. They have implications for the necessity for surgery, risks of surgery,
complications, aftercare, and expectations for improvement. Arthroscopic surgery
for acute injuries is less controversial because clear dysfunction and/or severe
instability are measurable indications for surgery and easily identifiable.
Surgery indications for pain management are largely for chronic damage and for
the milder grades or stages of acute injuries (severity Grade I and II). These
are controversial due to the existence of pain management and rehabilitation
alternatives. Arthroscopic surgery for pain management is currently under
debate.
Demographics
More than five and a
half million people visit orthopedic surgeons each year because of knee
problems. Over 600,000 arthroscopic surgeries are performed annually; 85% of
them are for knee surgery. One very common knee injury is a torn anterior
cruciate ligament (ACL) that often occurs in athletic activity. The most common
source of ACL injury is skiing. Approximately 250,000 people in the United
States sustain a torn or ruptured ACL each year. Research indicates that ACL
injuries are on the rise in the United States due to the increase in sport
activity.
The incidence of ACL
injuries in women is two to eight times greater than in men. While the exact
causes are not clear, differences in anatomy, strength, or conditioning are
thought to play major roles. Women also seem to be more prone to patella-femoral
syndrome (PFS), which is the inability of the patella to track smoothly with the
femur. PFS is due primarily to development of tendons that influence the ways in
which the knee tracks in movement. It can also be due to misalignments to other
parts of the lower body like foot pronation. Other ligament surgeries can be
caused by injury or overuse.
Knee dislocations are a
focus of recent research because of their increasing frequency. Incidences range
from 0.001% to 0.013% of all patients evaluated for orthopedic injuries. Many of
these injuries heal without treatment and go undetected. Many people with
multiple traumas in accidents have knee dislocations that go undiagnosed. Knee
dislocations are of special concern, especially in traumatic injury, because
their early diagnosis is required if surgery is to be effective. Knee
dislocations in the morbidly obese individuals often occur spontaneously and may
be associated with artery injury. This surgery involves complications related to
the obesity. Finally, knee dislocations have been reported to occur in up to 6%
of trampoline-associated accidents.
Description
Arthroscopic surgery for acute injuries
The knee bone sits
between the femur and the tibia, attached by four ligaments that keep the knee
stable as the leg moves. These ligaments can be damaged or torn through injuries
and accidents. Once damaged, they do not offer stability to the knee and can
cause buckling, or allow the knee to "give way." Ligaments can also "catch" and
freeze the knee or make the knee track in a different direction than its leg
movement, causing the knee to dislocate. Traumatic injuries such as automobile accidents may
cause more than one ligament injury, necessitating multiple repairs to
ligaments.
Four arthroscopic
procedures relate to damage to each of the four ligaments that stabilize the
knee joint movement. The four procedures are:
- Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL). A front-crossing ligament attaching the femur to the tibia through the knee; this ligament keeps the knee from hyperextension or being displaced back from the femur. The ACL is a rather large ligament that can withstand 500 lb (227 kg) of pressure. If it is torn or becomes detached, it remains that way and surgery is indicated. In the most severe cases, a graft to the ligament is necessary to reattach it to the bone. The surgery can use tissue from the patient, called an autograft, or from a cadaver, called an allograft. The patella tendon, which connects the patella to the tibia, is the most commonly used autograft. ACL reconstructive surgery involves drilling a tunnel into the tibia and the femur. The graft is then pushed through the tunnels and secured by stapling or sutures.
- Posterior cruciate ligament (PCL). A back-crossing ligament that attaches the front of the femur to back of the tibia behind the knee that keeps the knee from hyperextension or being displaced backward. PCL injuries are not as frequent as ACL injuries. These injuries are largely due to falls directly on the knee or hitting the knee on the dashboard of a car in an accident. Both displace the tibia too far back and tear the ligament. Surgery to the PCL is rare, because the tear can usually be treated with rest and with rehabilitation. If surgery is required, it is usually to reattach the PCL to the tibia bone.
- Medial collateral ligament (MCL). This is an inside lateral ligament connecting the femur and tibia and stabilizing the knee against lateral dislocation to the left or to the right. The injury is usually due to external pressure against the inside of the knee. In the case of a grade I or II collateral ligament tear, doctors are likely to brace the knee for four to six weeks. A grade III tear may require surgery to repair ligament tear and is followed by three months of bracing. Physical therapy may be necessary before resuming full activity.
- Lateral collateral ligament (LCL). An outside lateral ligament connecting the femur and tibia and stabilizing the knee against lateral dislocation. In the case of a grade I or II collateral ligament tear, doctors are likely to brace the knee for four to six weeks. A Grade III tear may require surgery to reattach the ligament to bone. Surgery will be followed by three months of bracing. Physical therapy may be necessary before resuming full activity.
Patello-femoral syndrome (PFS)
The patella rests in a
groove on the femur. Anything but a good fit can cause the patella to be
unstable in its movement and very painful. Some individuals have chronic
problems with the proper tracking of the patella with the femur. This may be
associated with conditions related to physical features like foot pronation, or
to types of body development in exercising or overuse of muscles. In the case of
damage, an examination of the cartilage surrounding the patella can identify
cartilage that increases friction as the patella moves. Smoothing the damaged
cartilage can increase the ease of movement and eliminate pain. Finally, a
tendon can occasionally make the patella track off center of the femur. By
moving where the tendon is attached through lateral release surgery, the patella
can be forced back into its groove.
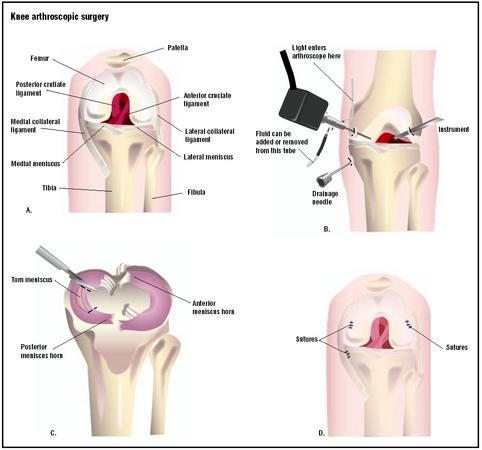
Step A shows the anatomy of
the knee from the front with the leg bent. To repair a torn meniscus, three
small incisions are made into the knee to admit laparoscopic instruments (B).
Fluid is injected into the joint to aid in the operation. The injury is
visualized via the instruments, and the torn area is removed (C). (
Illustration by GGS Inc.
Pain management with lavage and debridement
In addition to the
ligament and patella surgeries that are largely required for traumatic injuries,
arthroscopic surgery treats the wear and tear injuries related to a torn
meniscus, which is the crescent-shaped cartilage that cushions the knee, as well
as injuries to the surface of bone that makes joint movement painful. These are
related to osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
In lavage and
debridement, the surgeon identifies floating or displaced tissue pieces and
either flushes them out with a solution applied with arthroscopy or smoothes the
surface of bone to decrease pain. These two surgical treatments are
controversial because research has not indicated that alternatives to surgery
are not as successful.
All of the above
procedures are conducted through the visualization offered by the lighted
arthroscope that allows the surgeon to follow the surgery on a television
monitor. Instruments only about 0.15 in (4 mm) thick are inserted in a
triangular fashion around the knee. The arthroscope goes in one incision, and
instruments to cut and/or smooth and to engage in other maneuvers are put
through the other incisions. In this fashion, the surgeon has magnification,
perspective, and the ability to make tiny adjustments to the tissue without open
surgery. The triangular approach is highly effective and safe.
Diagnosis/Preparation
Disease and injury can
damage joints, ligaments, cartilage, and bone surfaces. Because the knee carries
most of the weight of the body, this damage occurs almost inevitably as people
age, due to sports injuries and through accidents.
The diagnosis of knee
injuries or damage includes a medical history, physical examination , x rays, and the
additional, more detailed imaging techniques with MRI or CT scan. Severe or
chronic pain and/or knee instability initially brings the patient to an
orthopedic physician. From there, the decision is made for surgery or for
rehabilitation. Factors that influence the decision for surgery are the
likelihood for repair and recovery of function, the patient's health and age,
and, most importantly, the willingness of the patient to consider changes in
lifestyle, especially as this relates to sport activity. Arthroscopic viewing is
the most accurate tool for diagnosis, as well as for some repairs. The surgeon
may provide only a provisional diagnosis until the actual surgery but will
apprise the patient of the most likely course the surgery will take.
Arthroscopic surgery
can be performed under local, regional, or general anesthetic. The type used
depends largely upon the severity of damage, the level of pain after surgery,
patient wishes, and patient health. The surgery is brief, less than two hours.
After closing the incisions, the leg will be wrapped tightly and the patient is
taken to recovery. For most same-day surgeries, individuals are allowed to leave
once the anesthetic effects have worn off. Patients are not allowed to drive.
Arrangements for pick up after surgery are mandated.
Unlike open surgery,
arthroscopic surgery generally does not require a hospital stay. Patients
usually go home the same day. Any crutches or canes required prior to surgery
will be needed after surgery. Follow-up visits will be scheduled within about a
week, at which point dressings will be removed.
Aftercare
Ligament- and patella-tracking surgeries
Arthroscopic surgery for severe ligament damage or knee displacement often involves ligament grafting. In some cases, this includes taking tissue from a tendon to use for the graft and drilling holes in the femur or tibia or both. Aftercare involves the use of crutches for six to eight weeks. A rehabilitation program for strengthening is usually suggested. Recovery times for resumed athletic activity are highly dependent on age and health. The surgeon often makes very careful assessments about recovery and the need for rehabilitation.
Patella-tracking
surgeries offer about a 90% chance that the patella will no longer dislocate.
However, many people have continued swelling and pain after surgery. These seem
to be dependent upon how carefully the rehabilitation plan is developed and/or
adhered to by the patient.
Lavage and debridement surgeries
Elevation of the leg
after surgery is usually required for a short period. A crutch or knee
immobilizer adds additional stability and assurance when walking. Physical
therapy is usually recommended to strengthen the muscles around the knee and to
provide extra support. Special attention should be paid to any changes to the
leg a few days after surgery. Swelling and pain to the leg can mean a blood clot
has been dislodged. If this occurs, the physician should be notified
immediately. Getting out of bed shortly after surgery decreases the risk of
blood clots.
Risks
The risks of
arthroscopic surgery are much less than open surgery, but they are not
nonexistent. The risk of any surgery carries with it danger in the use of
anesthesia, including heart attacks, strokes, pneumonia, and blood clots. The
risks are rare, but they increase with the age of the patient. Blood clots are
the most common dangers, but they occur infrequently in arthroscopic surgery.
Other risks include infections at the surgery site or at the skin level,
bleeding, and skin scars.
Risks related
specifically to arthroscopic surgery are largely ones related to injury at the
time of surgery. Arteries, veins, and nerves can be injured, resulting in
discomfort in minor cases and leg weakness or decreased sensation in more
serious complications. These injuries are rare. One major risk of arthropscopic
surgery to the knee for conditions related to tissue tears is that the pain may
not be relieved by the operation; it may even become worse.
Normal results
Normal results of
ligament surgery are pain, initial immobility and inflexibility, bracing of the
leg, crutch dependence, with increasing mobility and flexibility with
rehabilitation. Full recovery to the level of prior physical activity can take
up to three months. With ACL surgery, pain in the front of the knee occurs in
10–20% of individuals. Limited range of motion occurs in less than 5% due to
inadequate placement of the graft. A second surgery may be necessary.
Research indicates that
the pain-relieving effects for arthroscopic partial menisectomy (removal of torn
parts of cartilage) and debridement (the abrasion of cartilage to make it
smooth) are not very reliable. Pain relief varies between 50% and 75%, depending
upon the age, activity level, degree of damage, and extent of follow-up. One
study indicates that the two surgical procedures, lavage and debridement, fared
no better than no surgical procedure in relieving pain. The participants were
divided into three groups for arthroscopic surgery: one third underwent
debridement, a second third underwent lavage, and the remaining third likewise
were anesthetized and had three
incisions made in the knee area, though no procedure was performed. All three
groups reported essentially the same results. Each had slightly less pain and
better knee movement. The non-procedure had the best results. Debates about
normal expectations from minor arthroscopic surgery continue with many surgeons
believing that arthroscopic surgery of the knee should be restricted to acute
injuries.
Morbidity and mortality rates
Complications occur in less than 1% of arthroscopic surgeries. Different procedures have different complications. In general, morbidity results mostly from medically induced nerve and vascular damage; death or amputations almost never occur. Graft infection may occur, along with other types of infection largely due to microbes introduced with instruments. The latter cases are becoming increasingly rare as the science of arthroscopic surgery develops.
Alternatives
Whether or not surgical
treatment is the best choice depends on a number of factors and alternatives.
Age and the degree of injury or damage are key to deciding whether to have
surgery or rehabilitation. The physician calibrates the severity of acute
injuries and either proceeds to a determined treatment plan immediately or
recommends surgery. Alternatives for acute ligament injuries depend on the
severity of injury and whether the patient can make lifestyle changes and is
willing to move away from athletic activities. This decision becomes paramount
for many people with collateral and cruciate injuries.
According to the
American Association of Orthopedic Surgeons, conservative treatment for acute
injuries involves RICE: Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation, as well as a
follow-up rehabilitation plan. The RICE protocol involves resting the knee to
allow the ligament to heal, applying ice two or three times a day for 15–20
minutes, compression with a bandage or brace, and elevation of the knee whenever
possible. Rehabilitation requires range-of-motion exercises to increase
flexibility, braces to control joint immobility, exercise for quadriceps to support the
front of the thigh, and upper thigh exercise with a bicycle.
For arthritis-related
damage and pain management, anti-inflammatory
medication, weight loss, and exercise can all be crucial to strengthening the
knee to relieve pain. Evidence suggests that these alternatives work as well as
surgery.
Resources
BOOKS
Canale, S. Terry.
"Arthroscopic Surgery of Meniscus." In Campbell's Operative Orthopaedics.
9th ed. St. Louis: Mosby, Inc., 1998.
PERIODICALS
Alleyne, K. R., and M.
T. Galloway. "Osteochondral Injuries of the Knee." Clinics in Sports Medicine
20, no. 2 (April 2001).
Brown, C. H., and E. W.
Carson. "Revision Anterior Cruciate Ligament Surgery." Clinics in Sports
Medicine 18, no. 1 (January 1999).
Heges, M. S., M. W.
Richardson, and M. D. Miller. "The
Dislocated Knee." Clinics in Sports Medicine 19, no. 3 (July 2000).
Moseley, J. B, et al. "A Controlled Trial of Arthroscopic Surgery for Osteoarthritis of the Knee." New England Journal of Medicine 347, no. 2 (July 11, 2002): 81–88.
Vangsness, C. T., Jr. "Overview of Treatment Options for Arthritis in the Active Patient." Clinical Sports Medicine 18, no. 1 (January 1999): 1–11.
ORGANIZATIONS
American Academy of
Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS). 6300 North River Rd. Suite 200, Rosemont, IL 60018.
(847) 823-7186 or (800) 346-2267; Fax: (847) 823-8125. http://www.aaos.org .
Arthritis Foundation.
P.O. Box 7669, Atlanta, GA 30357-0669. (800) 283-7800. http://www.arthritis.org .
National Institute of
Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases Information Clearinghouse. 1 AMS
Circle, Bethesda, MD 20892-3675. (301) 495-4484 or (877) 226-4267; Fax: (301)
718-6366; TTY: (301) 565-2966. http://www.nih.gov/niams .
OTHER
"Arthroscopic Knee
Surgery No Better Than Placebo Surgery." Medscape Medical News. July 11,
2002. http://www.medscape.com .
"Arthroscopic Surgery." Harvard Medical School Consumer Health. InteliHealth. http://www.intelihealth.com .
"Knee Arthroscopy
Summary." Patient Education Institute, National Library of
Medicine/NIH/MedlinePlus. .
POSTED BY ATTORNEY RENE G. GARCIA:
For more information:- Some of our
clients have suffered injuries that require Knee Arthroscopic Surgery due to a
serious accident. The Garcia Law Firm, P.C. was able to successfully
handle these types of cases. For a free consultation please call us at 1-866-
SCAFFOLD or 212-725-1313.
No comments:
Post a Comment